מיכשור תעשייתי - Purified Water
Reverse osmosis is often used as a preparation for secondary demineralisation, either by means of a second reverse osmosis stage or a continuous electro-deionisation stage.
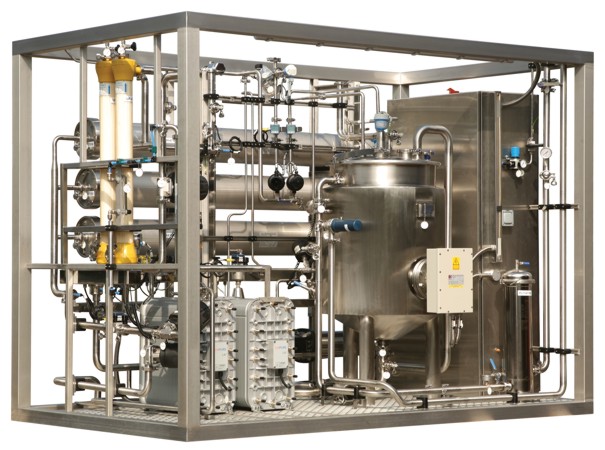
The reverse osmosis module has semipermeable membranes that physically inhibit or reject the flow of certain contaminants. The membranes not only capture some particles but also share them.
Reverse osmosis is a separation technique of great value as it can eliminate up to 98% of dissolved ions, in addition to bacteria, particles, pyrogens and organic matter. The separation membrane is manufactured from thin-layer polyamide with very high percentages of rejection and is quite sensitive to chemical degradation particularly of chemical compounds that contain chlorine.
Electro-Deionisation
Continuous electro-deionisation uses a combination of ion exchange resins and membranes assembled as a sandwich between two electrodes [anode (+) and cathode (-)] subjected to a DC electric potential difference, which forces the continuous migration of ions from the feed chamber to the connecting concentration chambers. This potential also breaks down the water molecules producing hydrogen ions and hydroxyls which continuously bring about the regeneration of the resin (no reagents are used for regeneration). The elimination of regeneration times gives advantages to this purification method, as continuous production is achieved without stoppages.
The main characteristic of purified water is the low level of contaminants such as:↓
- Dissolved organic matter
- Solids in suspension
- Micro-organisms
- Colloidal content
- Gases
The most important parameters to be checked and regulated according to the various pharmacopoeias are:↓
- Conductivity
- Microbiology
- Total Organic Carbon (TOC)
- Endotoxins (LAL)
לקבלת הצעת מחיר על מוצר
Purified Water
לקוח\ה יקר\ה שלום,
נציגינו עומדים לשירותך בכל עת כדי לענות לפנייתך.
לנוחיותך מספר שיטות התקשרות עמנו, על מנת, שנוכל לתת לך את השירות הטוב ביותר:
ליצור קשר באמצעות אי מייל sales@master-cold.co.il או באמצעות מילוי פרטים באתר.
אנא מלא את פרטיך, את נושא הפנייה ואת פרטי ההתקשרות המלאים ואנו נדאג לטפל בפנייתך בכל תשומת הלב ובהקדם האפשרי.
במידה ולא נענית תוך פרק זמן סביר, תוכל\י לברר את סטטוס בקשתך באמצעות קשר טלפוני 1-800-22-22-66
 249 קולות, בממוצא
9.2 נקודות מ10 נקודות.
249 קולות, בממוצא
9.2 נקודות מ10 נקודות.